HRUweb Tutorial
The WebHRU is a web tool which was developed to derivate hydrological response units (HRU) online. It was implemented in Python and calculates HRUs according to opensource GRASS-GIS algorithms.
After every processing step, the results are provided as raster or shape data which are all compatible with established GIS formats.
For this tutorial, sample data from Rio de Janeiro in Brazil were used.
Contents |
Starting WebHRU Tool
Link to HRU Tool: http://intecral.uni-jena.de/hruweb
Structure of HRUWeb user interface
The map window is located in the centre. By using the arrow buttons or the +/- tool bar in the top left, the view can be set manually. The remaining items are located around the map:
- Table of Layers
- By right-clicking on the overlays,the layers can either be zoomed or removed.
- By using drag and drop, the order of layer visibility can be changed.
- Map Legend (→ Map Legend Description see below)
- Wizard: processing step description and manual input/settings. Includes the buttons for 'Run' and 'Next'.
- Server Log and Results: shows the uploading process & provides the result layer as raster or shape file.
Map Legend Description
- Remove layer
- Zoom to map extend: restores smallest possible scale of the map
- Zoom in the map (
 ) or zoom out of the map (
) or zoom out of the map ( )
)
- Zoom to previous map extend (backward
 forward)
forward)
- Create bounding box of interest (→ section Step 2)
- Relocate gauge (→ section Step 6)
- User login (→ NEXT STEP)
Step 0: Data Preparations
First of all: Do user login!
Otherwise, your work will not be saved!
Check your input data!
Then, open your input data in a GIS and check them for:
- completeness: At least DEM and gauges are required for delineating HRUs. The rasters of landuse, soil and geology are optional input.
- projection: The coordinate system has to be metric (like e.g. UTM) in order to enable distance calculations.
- layer extend: The layers should have at least the size of the catchment. A base map could be helpful.
| Input data | Description | Format | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | Raster of Digital Elevation Model | Tiff (.tif) or .zip-file | mandatory |
| Gauges | Layer of gauging stations | .zip-file | mandatory |
| Landuse | Raster of landuse | Tiff (.tif) or .zip-file | optional |
| Soil | Raster of soil | Tiff (.tif) or .zip-file | optional |
| Geology | Raster of geology | Tiff (.tif) or .zip-file | optional |
The following sections describe the single substeps in the WebHRUTool. Each substep is divided into the subsections Aim, Procedure and Results.
Step 1: Define Input Data
Aim: Upload input data or choose data via catalog.
Procedure:
- The required input data are described in Step 0.
- You have two options to define the dem input data:
- Upload your own local input data
- or
- Use input data via catalog: choose the DEM you need by clicking on 'add'.
- Note:The chosen DEM is listed in the Table of Layers as a new layer. You can edit it by clicking on the layer and using the Map Legend.
 →
→ 
- The projection of the map will be set automatically on the basis of the input data.
- For starting the uploading process, click 'Run' in the Wizard.
Results:
- The overlays 'Upload' and 'Gauges' are created.


- //Note: If the 'Upload' or the 'Gauges' layer are removed, the whole uploading procedure has to be done again by reloading the page.
- They can be downloaded from data browser.
- File:Databrowser step1.png
When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 2: Data Setup
Aim: Define area of interest for delineating HRUs.
Procedure:
- To zoom into the area of interest, right-click on the 'Upload' layer and choose 'Zoom to layer extend' or use the magnifier to do so.
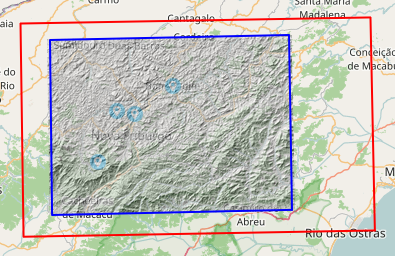
- The gauges are shown in light blue dots. The area of the gauges is marked automatically in a red bounding box.
- //Note: The red box marks the maximum extend. Data outside of this extend are not delineated.
- If the red bounding box does already represent your region of interest, you can skip the next step and click 'Run'.
- By clicking on the symbol, another overlay layer called 'Region' is created and the automatically set bounding box is now covered by a blue box.
- This blue box represents the area that should be used for delineating HRUs later on. Due to computational reasons, its extend should
- be fitted to the gauges' positions.
- Fit it by clicking on the outline of the blue box and move it at the blue crosses.
- In order to shift the whole box, drag&drop it by the blue cross in the centre.
- In order to resize the box, use the cross at the side.
- //Note: The 'Region' layer can be removed without problems. To do so, right-click on the layer and choose "remove".
By clicking on , the region layer can be restored again.
, the region layer can be restored again.
- //Note: If the extend of the blue box is chosen too small, important parts for delineating HRUs could be left out which makes the results unusable.
- For starting the process, click 'Run'.
Results:
- A 'Hillshade' overlay is created.
- The hillshade layer can be downloaded from data browser.
When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 3: Data Preparation
Aim: Preprocess the DEM by filling its sinks.
- If the DEM was already preprocessed that way, no sink filling is necessary.
- Otherwise, it is recommended to do so in order to prevent lack of data.
Procedure:
- Choose "Filling" (default), if the sinks should be filled or "No filling", if they should not be filled.

- For starting the process, click 'Run'.
Results:
- A DEM with filled sinks is created.
- File:Overlays step3.png
- File:Filled dem.png
- Single maps of sinkless elevation, slope and aspect can be downloaded from data browser.
- //Note: If filling fails, no maps for slope and aspect are available.
When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 4: Reclassification
Aim: Reclassify terrain attributes.
Procedure:
- In this step, the class ranges of slope and aspect can be reclassified and renamed.
- In order to change table entries, click in the concerning field and type in the desired value.
- "Old": lists all existing class ranges
- "New": assigns IDs to classes
- For starting the process, click 'Run'.
Result:
When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 5: Waterflow
Aim: Define resolution of the stream network/ river system.
Procedure:
- With each subbasin, one river segment is created. In this step, the maximum number of cells (pixels) for a subbasin of the smallest size has to be specified.
- File:Eingabe der pixelzahl.png
- example 10.000
- For starting the process, click 'Run'.
Results:
- The layers 'Streams' and 'Subbasins' are created.

- You can download a zip file of stream network + subbasin layer from data browser

When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 6: Outlets
Aim: Check the gauges' position and decide which gauges should be considered.
- While creating the subbasins, the gauges' position can differ from the stream network.
Procedure:
- First of all, use the drag and drop mechanism to change the visibility of the layers in the layer view (→ section Starting the Webtool).
- Order the layer of gauges on top, followed by the layer of river network.

- Open Google Earth and zoom in to the gauges. Now use the gauges' position in Google Earth
- as a reference and relocate the gauges in the map of your results.

- Now the tool for relocating gauges had to be activated. Click on
 in the legend to activate it.
in the legend to activate it.
- In order to relocate a gauge, click on a gauge and drag it to the proper river segment.

- //Note: For every gauge on a river segment, a catchment is created. If a gauge should not be considered in the further delineation of HRUs, just drag it out of the blue bounding box.
- File:OutOfBB.png
- For starting the process, click 'Run'.
Results:
When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 7: Dataoverlay & Generalization
Aim: Computing HRUs.
Procedure:
- In this step, all data layer are calculated to one HRU layer by the WebTool.
- No user activity is required here.
Results:
- The layer 'HRU' is created in the layer overview.

- A map of the created HRUs is provided in the data browser

When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 8
Results:
- Statistics per HRU
Help Section
How to ...
- Step 4: choose the best settings for ranges of values of slope and aspect
- Step 5: choose the best settings for number of pixels for the smallest subbasin
- Step 6: decide, if a gauge should be considered or not?
---> in farbig hinterlegten Kästchen?
Fragen:
- Hilfe Abschnitte auf die Schritte aufteilen oder einen ganzen Abschnitt für alle?