HRUweb Tutorial
(→Step 6: Outlets) |
(→Step 6: Outlets) |
||
| Line 240: | Line 240: | ||
:Locate the layer of gauges on top, followed by the layer of river network. | :Locate the layer of gauges on top, followed by the layer of river network. | ||
:Open Google Earth and zoom in to the gauges. Now use the gauges' position in Google Earth | :Open Google Earth and zoom in to the gauges. Now use the gauges' position in Google Earth | ||
| − | as a reference and relocate the gauges in the map of your results. | + | :as a reference and relocate the gauges in the map of your results. |
:To relocate a gauge click on it and drag it to the proper river segment. | :To relocate a gauge click on it and drag it to the proper river segment. | ||
Revision as of 14:30, 9 April 2017
The WebHRU is a web tool which was developed to derivate hydrological response units (HRU) online. It was implemented in Python and calculates HRUs according to GRASS-GIS algorithms.
Fragen:
- Bezeichnung der 2. Unterteilung: Workflow oder Parameter Setting?
- Legend description am Anfang?
Contents |
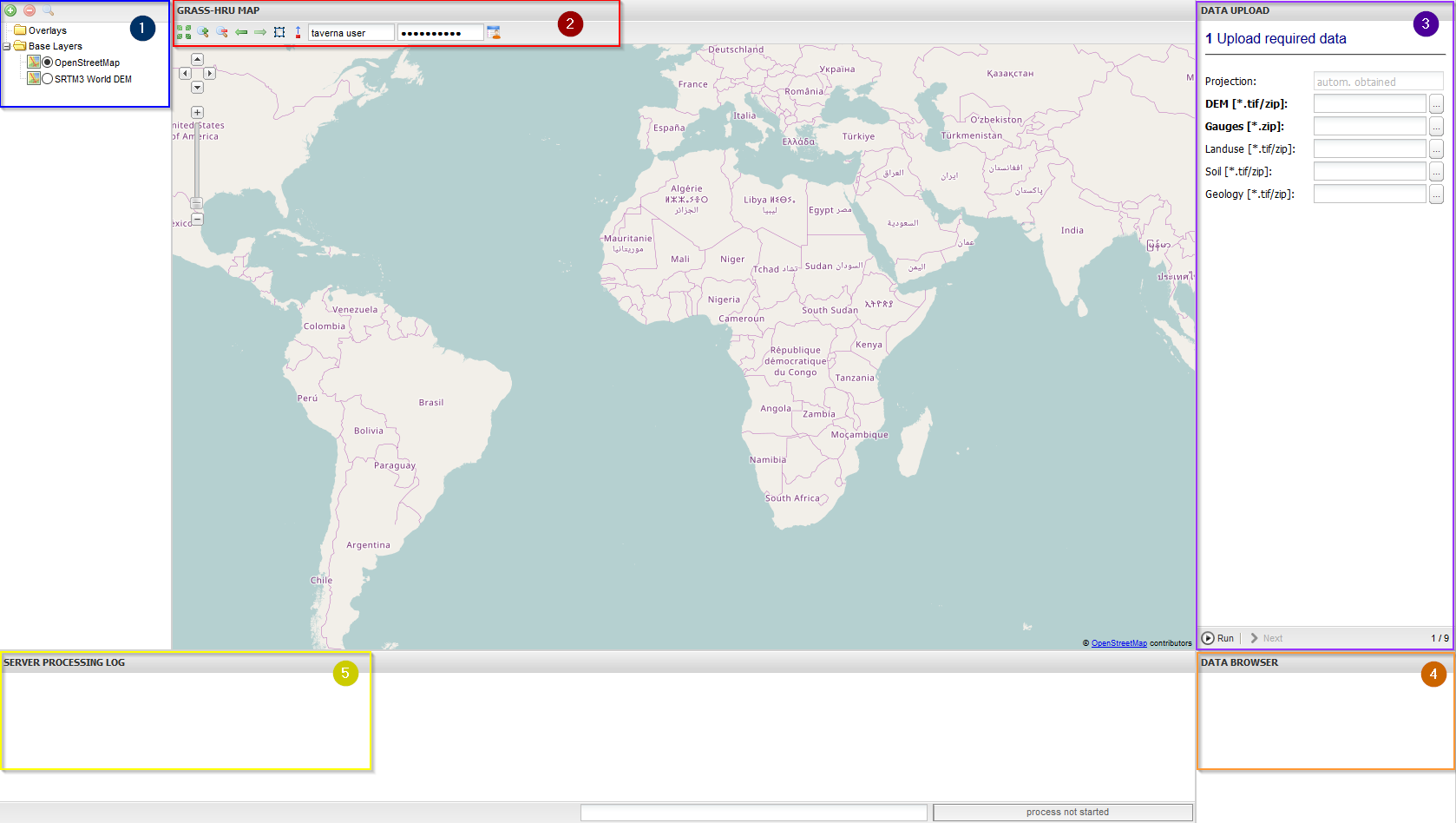
Starting WebHRU Tool
Link to HRU Tool: http://intecral.uni-jena.de/hruweb
Description of user interface:
- map window
- table of layers (set visibility, zoom in or remove -> see section "Legend") [set link to legend]
- process log
- download browser (provides data layer as raster or shape file)
- processing step description and manual input/settings
- The uploading process is always shown in the Server Processing Log:
Step 0: Data Preparations
First of all, open your input data in a GIS and check them for:
- completeness: At least DEM and gauges are required for delineating HRUs. The rasters of landuse, soil and geology are optional input.
- projection: The coordinate system has to be metric (like e.g. UTM) in order to enable distance calculations.
- layer extend: The layers should have at least the size of the catchment. A base map could be helpful.
| Input data | Description | Format | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | Raster of Digital Elevation Model | Tiff (.tif) or .zip-file | mandatory |
| Gauges | Layer of gauging stations | .zip-file | mandatory |
| Landuse | Raster of landuse | Tiff (.tif) or .zip-file | optional |
| Soil | Raster of soil | Tiff (.tif) or .zip-file | optional |
| Geology | Raster of geology | Tiff (.tif) or .zip-file | optional |
Step 1: Uploading Input Data
Aim: Define base map and upload input data
Parameter Settings/ Workflow:
- At first, decide which map source should be used as the base layer (default: OpenStreetMap):
- Then, upload the required input data (required data described in Step 0).
- The projection of the map will be set automatically on the basis of the input data.
- For starting the uploading process, click 'Run'.
Results:
- The overlays 'Upload' and 'Gauges' are created.


- //Note: If the 'Upload' or the 'Gauges' layer are removed, the whole uploading procedure has to be done again by reloading the page.
- They can be downloaded from data browser.
- File:Databrowser step1.png
When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 2: Data Setup
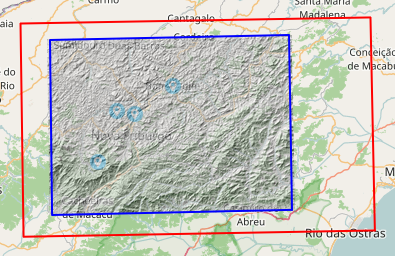
Aim: Define area of interest for delineating HRUs
Parameter Settings/Workflow:
- To zoom into the area of interest, right-click on the 'Upload' layer and choose 'Zoom to layer extend' or use the magnifier to do so.
- The gauges are shown in light blue dots. The area of the gauges is marked automatically in a red bounding box.
- //Note: The red box marks the maximum extend. Data outside of this extend are not delineated.
- If the red bounding box does already represent your region of interest, you can skip the next step and click 'Run'.
- By clicking on the symbol, another overlay layer called 'Region' is created and the automatically set bounding box is now covered by a blue box.
- This blue box represents the area that should be used for delineating HRUs later on. Due to computational reasons, its extend should
- be fitted to the gauges' positions.
- Fit it by clicking into the blue box and move it at the blue crosses.
- In order to shift the whole box, drag&drop it by the blue cross in the centre.
- In order to resize the box, use the cross at the side.
- //Note: The 'Region' layer can be removed without problems. To do so, right-click on the layer and choose "remove".
By clicking on , the region layer can be restored again.
, the region layer can be restored again.
- //Note: If the extend of the blue box is chosen too small, important parts for delineating HRUs could be left out which makes the results unusable.
Results:
- A 'Hillshade' overlay is created.
- The hillshade layer can be downloaded from data browser.
When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 3: Data Preparation
Aim: Preprocess the DEM by filling its sinks.
- If the DEM was already preprocessed that way, no sink filling is necessary.
- Otherwise, it is recommended to do so in order to prevent lack of data.
Parameter Settings/ Workflow:
Results:
- A DEM with filled sinks is created.
- File:Overlays step3.png
- File:Filled dem.png
- Single maps of sinkless elevation, slope and aspect can be downloaded from data browser.
- //Note: If filling fails, no maps for slope and aspect are available.
When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 4: Reclassification
Aim: Reclassify terrain attributes.
Parameter Settings/ Workflow:
- In this step, the class ranges of slope and aspect can be reclassified and renamed.
- In order to change table entries, click in the concerning field and type in the desired value.
- "Old": lists all existing class ranges
- "New": assigns IDs to classes
Result:
When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 5: Waterflow
Aim: Define resolution of the stream network/ river system.
Parameter Settings/ Workflow:
- With each subbasin, one river segment is created. In this step, the maximum number of cells (pixels) for a subbasin of the smallest size has to be specified.
- File:Eingabe der pixelzahl.png
- example 10.000
Results:
- The layers 'Streams' and 'Subbasins' are created.

- You can download a zip file of stream network + subbasin layer from data browser

When finished, click 'Next'.
Step 6: Outlets
Aim: While creating the subbasins, the gauges' position can differ from the stream network.
- Check the gauges' position and decide which gauges should be considered.
Workflow:
- First of all, use the drag and drop mechanism to change the visibility of the layers in the layer view (legend no. X).
- Locate the layer of gauges on top, followed by the layer of river network.
- Open Google Earth and zoom in to the gauges. Now use the gauges' position in Google Earth
- as a reference and relocate the gauges in the map of your results.
- To relocate a gauge click on it and drag it to the proper river segment.
click on ![]() and locate gauges on the right stream segment
and locate gauges on the right stream segment
Legend
The layers can be edited in overview in the top left. By right-clicking on the overlays, the layers can either be zoomed or removed. By using drag and drop in the overlay list, the order of layer visibility can be changed.
== How to choose the best settings for ranges, HRU size+amount ==