GRASS-HRU
From ILMS-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Vorbereitung) |
(→Download) |
||
| (84 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[de:GRASS-HRU]] |
| + | [[pt:GRASS-HRU]] | ||
| + | [[File:Grasshru.png|thumb|rechts|GRASS-HRU]] The complete process chain for the HRU derivation was implemented according to a service-oriented application in GRASS-GIS. The execution environment is strictly separated from the operating environment by using a preconfigured, virtual machine which is in charge of data preparation and the calculation of HRUs in GRASS-GIS. A plug-in developed for QGIS creates an intuitive, wizard-driven and transparent environment for the execution of the process chain. | ||
| − | ==Download | + | == Download/Installation of GRASS-HRU== |
| − | === | + | === Download === |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Use the installation package for a complete and easy installation: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | ! !! Download | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | Installer (Windows) || [<!--http://www.geoinf.uni-jena.de/~c3schs/grass-hru/ILMS-3.1.zip-->http://jams.uni-jena.de/ilmswiki/files/ILMS_v3.1_2.zip ILMS_v3.1_2.zip] | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | + | (follow the instructions given [[GRASS-HRU_Manual_install|here]] to do a manual installation of GRASS-HRU) | |
| − | [[ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | === Installation === |
| − | + | For installing the GRASS-HRU software package, please follow these steps: | |
| − | # | + | # Unpack the downloaded GRASS-HRU archive in your desired location |
| − | + | # <span style="color:red;">Currently, the automatic detection of 32/64 bit system failed in some cases - so it is recommended to edit the setup.cfg manually ("version" in section "general": "32bit" or "64bit")</span> | |
| − | # | + | # Choose the setup file (setup.exe) and execute it as an administrator (right click the file -> Execute as Administrator) |
| − | # | + | # Whenever asked for permission to install software/drivers during setup, please confirm |
| − | + | # During installation, you are prompted to restart the computer – please quit setup, reboot and restart the setup script (with administrator rights) again | |
| − | # | + | # Once the installation has finished, close the installer by pressing the "exit setup" button |
| − | # | + | |
| − | == | + | ==Starting GRASS-HRU== |
| − | + | In order to start the HRU delineation process, please start GRASS-HRU as follows: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # From the GRASS-HRU installation folder, please start the GRASS-HRU Launcher by double-clicking GRASS-HRU.exe | |
| − | # | + | # From the menu bar, start the GRASS server appliance by clicking the green start icon and wait, until the appliance has fully booted |
| − | # | + | # Press the GRASS-HRU@QGIS button to launch the bundled QGIS version |
| + | # Activate the GRASS-HRU plugin in QGIS by following these steps: | ||
| + | #* choose "Plugins -> Manage Extension..." from the QGIS menu | ||
| + | #* tick the checkbox in front of GRASS-HRU | ||
| + | # Start the GRASS-HRU wizard by choosing its launcher button from the toolbar: [[File:Grasshru.png|30x30px|text-bottom]] | ||
| + | # After you have finished using GRASS-HRU, stop the GRASS server appliance by clicking the red stop button | ||
| − | ==Details | + | ==Details on the HRU Derivation Using the Wizard== |
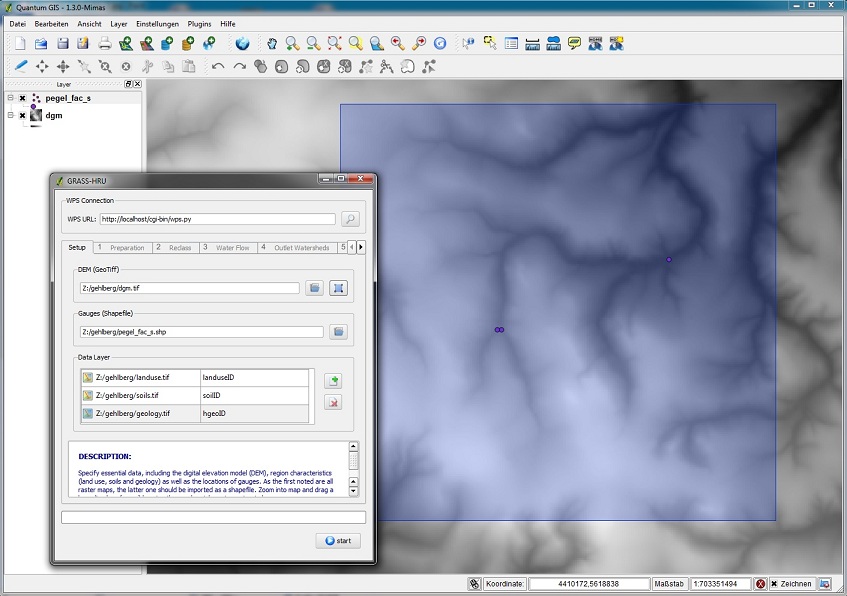
| − | === | + | ===Step 0: Setup=== |
| − | * | + | *Selection of the digital terrain model (DGM) in GeoTiff format and a shapefile format, each by using the button ''Datei'' next to the input field. |
| − | * | + | *Selection of additional data layers (land use, soil, geology) by clicking on the add button on the right hand side of the ''Data Layer'' chart. For each of the entries, right click it and choose the appropriate parameter file name |
| − | * | + | *Opening a bounding box (first left mouse click: top left-hand corner, second left mouse click: bottom right-hand corner, right mouse click: delete bounding box). The resulting bounding box should comprise the complete catchment area to be analysed. |
| − | [[ | + | [[File:Grass_hru_2.jpg]] |
| − | === | + | |
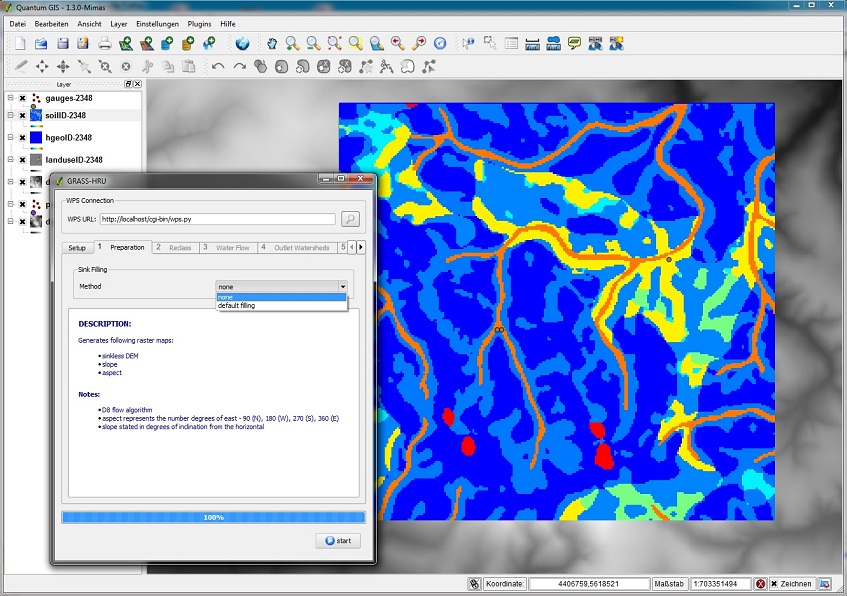
| − | * | + | ===Step 1: Preparation=== |
| − | * | + | *It is possible to delete local sinks from the DGM. In case the current DGM has not been filled yet, ''default filling'' should be selected from the methodology list. |
| − | [[ | + | *For the calculation of slope and slope orientation no further input is necessary. |
| − | === | + | [[File:Grass_hru_3.jpg]] |
| − | * | + | |
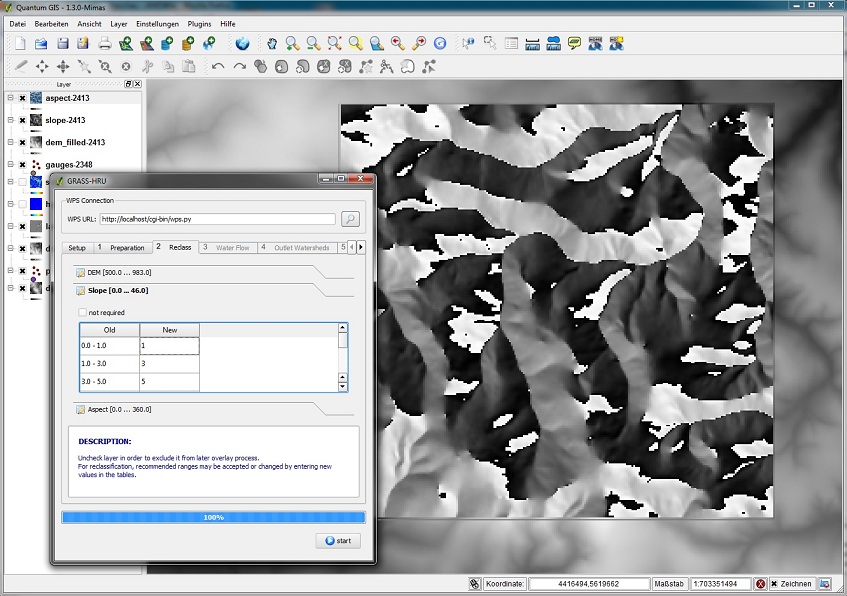
| − | * | + | ===Step 2: Reclass=== |
| − | * | + | *According to the different indices (DEM, Slope and Aspect) the corresponding map is classified. |
| − | [[ | + | *The standard areas and values can be applied or modified. In case of a modification values cannot be below or above the corresponding minima and maxima. |
| − | === | + | *If a data set should not be used for HRU derivation, it can be deselected (Checkbox ''not required''). |
| − | * | + | [[File:Grass_hru_4.jpg]] |
| − | * | + | |
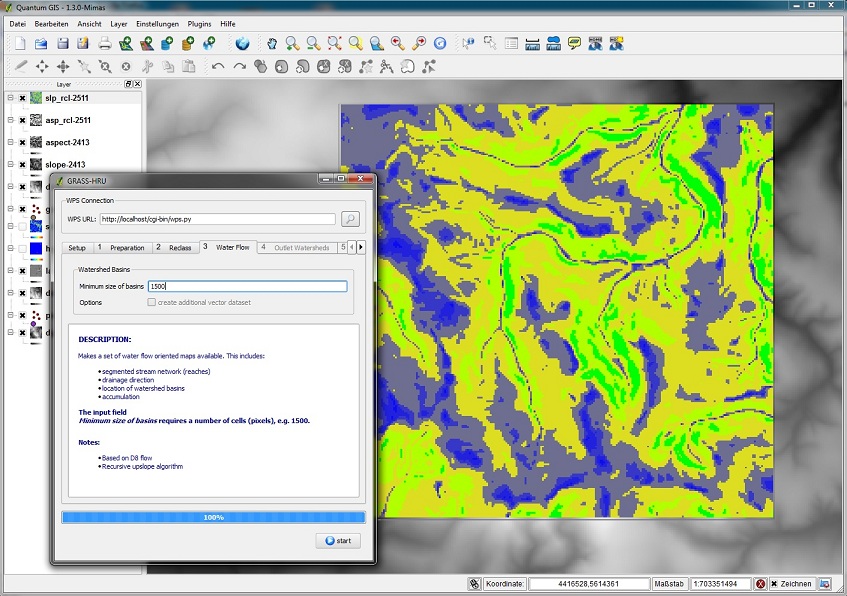
| − | * | + | ===Step 3: Waterflow=== |
| − | [[ | + | *For the derivation of the water supply network, flow accumulation and flow direction and for partial catchment areas a threshold value ''Minimum Size Of Basins'' is required. |
| − | === | + | *This parameter determines, for example, the degree of detail of the water network or the number of partial catchment areas. The threshold value determines the smaller, derivable partial catchment area and is indicated in cells (number of pixels). |
| − | * | + | *Example: A value of 1500 (and an assumed solution of 25m) results in a designation of partial catchment areas bigger than (1500*25*25)/1000000 = 0.9375km² ~ 1km². |
| − | *# | + | [[File:Grass_hru_5.jpg]] |
| − | *# | + | |
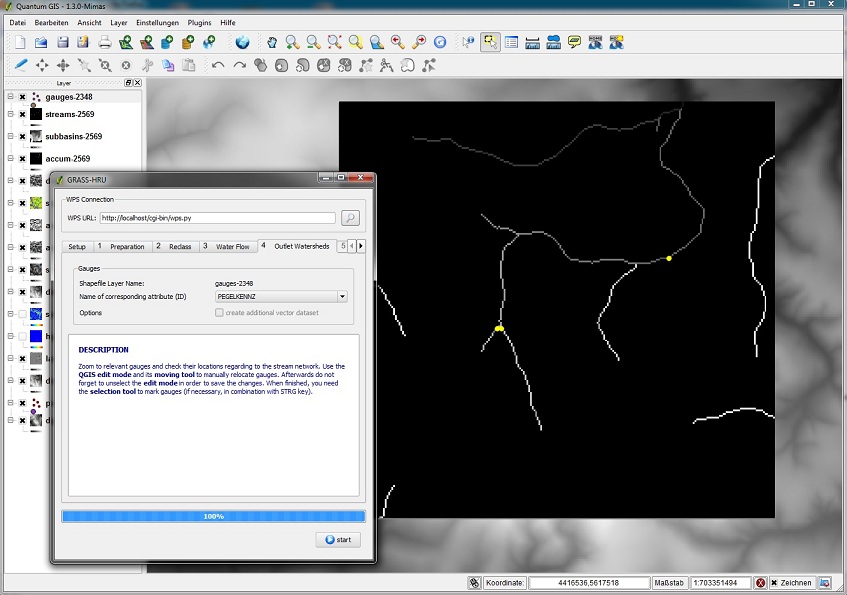
| − | *## | + | ===Step 4: Outlet Watersheds=== |
| − | *## | + | *The following steps are necessary for the calculation of a map showing partial watersheds derived from their water levels: |
| − | *## | + | *#Pan the water level and supply map up in the key, so both data sets are visible. |
| − | *# | + | *#Check with the zoom tool whether the singular water levels lie exactly on the derived water supply network. If not, modify the level layer until '''all levels in the watershed''' lie on the water sections. To do so, please proceed as follows: |
| − | * | + | *##Select the level layer on the key and activate the vector editing mode of QuantumGIS [[File:Qgis_tool_1.jpg|30px]] |
| − | [[ | + | *##Take the tool for panning vector points [[File:Qgis_tool_2.jpg|30px]] and relocate the corresponding watersheds |
| − | === | + | *##Finally, cancel the edit mode by clicking on [[File:Qgis_tool_1.jpg|30px]] again and agree to save changes |
| − | * | + | *#If all water levels in the catchment area have the correct position in the water network, those levels relevant to the calculation have to be selected - use the marker tool [[File:Qgis_tool_3.jpg|30px]]. |
| − | * | + | *Choose the shapefile attribute on the selection list ''Name of corresponding attribute (ID)'' which represents a unique parameter for the level ('''integer and > 0''', e.g. level ID). |
| − | * | + | [[File:Grass_hru_6.jpg]] |
| − | [[ | + | |
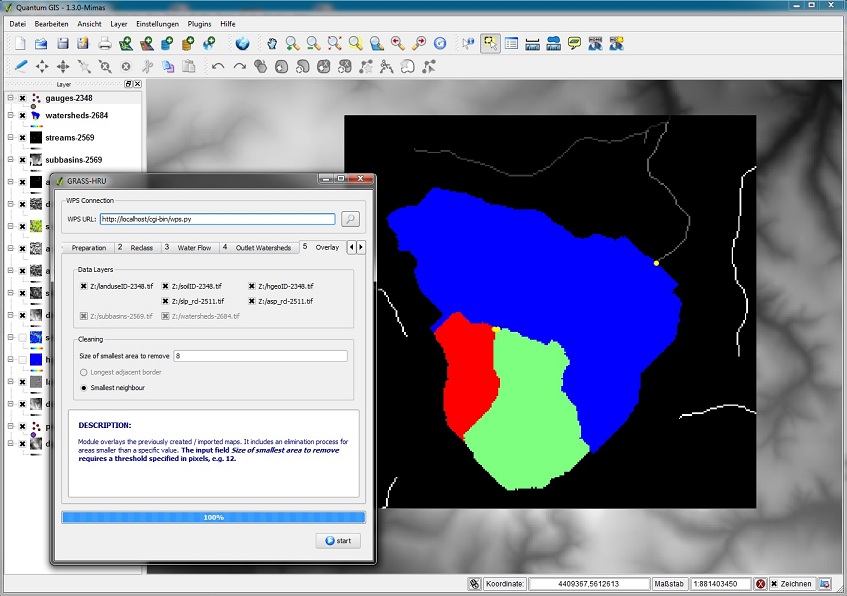
| − | === | + | ===Step 5: Overlay=== |
| − | * | + | *The intersection of all data layers creates small areas (specific layers can be disregarded by deselecting them). Those areas are not suitable as HRUs and should therefore be eliminated. |
| − | * | + | *For this purpose a threshold value is defined (''Size of smallest area to remove'') which determines the minimum size of an HRU (in cells). |
| − | ** | + | *Example: A value of 8 (and an assumed solution of 25m) results in a designation of HRUs which is bigger than (8*25*25) = 5000m² =0.5ha |
| − | ** | + | [[File:Grass_hru_7.jpg]] |
| − | ** | + | |
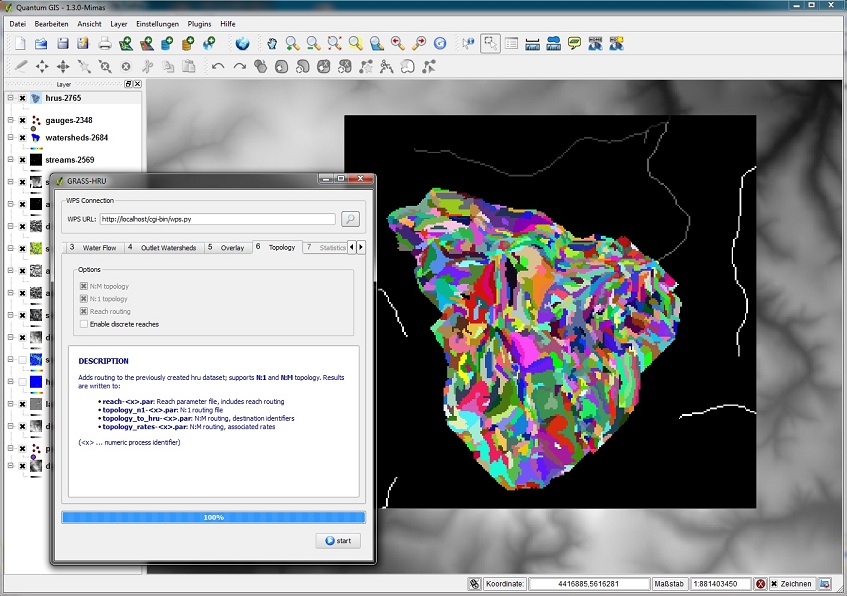
| − | * | + | ===Step 6: Topology=== |
| − | [[ | + | *For the determination of the topological connection of HRUs (and water segments) no specific parameter input is necessary. |
| − | === | + | *The module calculates |
| − | * | + | **the N:1 topology (HRUs can drain in only one neighboring HRU/river section) |
| − | [[ | + | **the N:M topology (HRUs can drain in several neighboring HRUs/river sections) |
| + | **water topology (topological combination of all river sections) | ||
| + | *The option ''Enable discrete reaches'' is an extension of the topological derivation and its development has not yet been finished. | ||
| + | [[File:Grass_hru_8.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
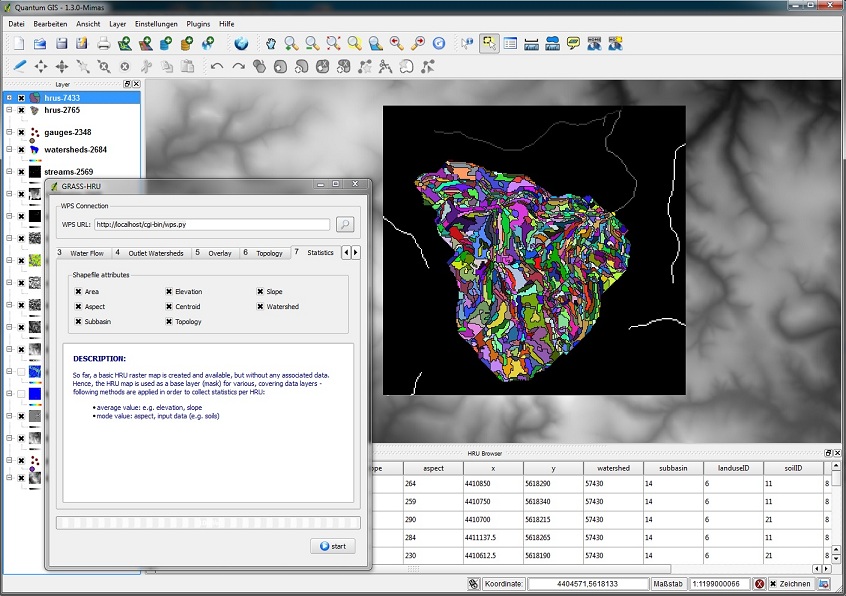
| + | ===Step 7: Statistics=== | ||
| + | *The existing HRU map in grid format (Geo Tiff) is now converted into a shapefile. In doing so, additional features of a single HRU can be selected which are taken to the attribute chart or are supposed to be calculated. | ||
| + | [[File:Grass_hru_9.jpg]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:05, 4 March 2019
The complete process chain for the HRU derivation was implemented according to a service-oriented application in GRASS-GIS. The execution environment is strictly separated from the operating environment by using a preconfigured, virtual machine which is in charge of data preparation and the calculation of HRUs in GRASS-GIS. A plug-in developed for QGIS creates an intuitive, wizard-driven and transparent environment for the execution of the process chain.Contents |
Download/Installation of GRASS-HRU
Download
Use the installation package for a complete and easy installation:
| Download | |
|---|---|
| Installer (Windows) | ILMS_v3.1_2.zip |
(follow the instructions given here to do a manual installation of GRASS-HRU)
Installation
For installing the GRASS-HRU software package, please follow these steps:
- Unpack the downloaded GRASS-HRU archive in your desired location
- Currently, the automatic detection of 32/64 bit system failed in some cases - so it is recommended to edit the setup.cfg manually ("version" in section "general": "32bit" or "64bit")
- Choose the setup file (setup.exe) and execute it as an administrator (right click the file -> Execute as Administrator)
- Whenever asked for permission to install software/drivers during setup, please confirm
- During installation, you are prompted to restart the computer – please quit setup, reboot and restart the setup script (with administrator rights) again
- Once the installation has finished, close the installer by pressing the "exit setup" button
Starting GRASS-HRU
In order to start the HRU delineation process, please start GRASS-HRU as follows:
- From the GRASS-HRU installation folder, please start the GRASS-HRU Launcher by double-clicking GRASS-HRU.exe
- From the menu bar, start the GRASS server appliance by clicking the green start icon and wait, until the appliance has fully booted
- Press the GRASS-HRU@QGIS button to launch the bundled QGIS version
- Activate the GRASS-HRU plugin in QGIS by following these steps:
- choose "Plugins -> Manage Extension..." from the QGIS menu
- tick the checkbox in front of GRASS-HRU
- Start the GRASS-HRU wizard by choosing its launcher button from the toolbar:

- After you have finished using GRASS-HRU, stop the GRASS server appliance by clicking the red stop button
Details on the HRU Derivation Using the Wizard
Step 0: Setup
- Selection of the digital terrain model (DGM) in GeoTiff format and a shapefile format, each by using the button Datei next to the input field.
- Selection of additional data layers (land use, soil, geology) by clicking on the add button on the right hand side of the Data Layer chart. For each of the entries, right click it and choose the appropriate parameter file name
- Opening a bounding box (first left mouse click: top left-hand corner, second left mouse click: bottom right-hand corner, right mouse click: delete bounding box). The resulting bounding box should comprise the complete catchment area to be analysed.
Step 1: Preparation
- It is possible to delete local sinks from the DGM. In case the current DGM has not been filled yet, default filling should be selected from the methodology list.
- For the calculation of slope and slope orientation no further input is necessary.
Step 2: Reclass
- According to the different indices (DEM, Slope and Aspect) the corresponding map is classified.
- The standard areas and values can be applied or modified. In case of a modification values cannot be below or above the corresponding minima and maxima.
- If a data set should not be used for HRU derivation, it can be deselected (Checkbox not required).
Step 3: Waterflow
- For the derivation of the water supply network, flow accumulation and flow direction and for partial catchment areas a threshold value Minimum Size Of Basins is required.
- This parameter determines, for example, the degree of detail of the water network or the number of partial catchment areas. The threshold value determines the smaller, derivable partial catchment area and is indicated in cells (number of pixels).
- Example: A value of 1500 (and an assumed solution of 25m) results in a designation of partial catchment areas bigger than (1500*25*25)/1000000 = 0.9375km² ~ 1km².
Step 4: Outlet Watersheds
- The following steps are necessary for the calculation of a map showing partial watersheds derived from their water levels:
- Pan the water level and supply map up in the key, so both data sets are visible.
- Check with the zoom tool whether the singular water levels lie exactly on the derived water supply network. If not, modify the level layer until all levels in the watershed lie on the water sections. To do so, please proceed as follows:
- If all water levels in the catchment area have the correct position in the water network, those levels relevant to the calculation have to be selected - use the marker tool
 .
.
- Choose the shapefile attribute on the selection list Name of corresponding attribute (ID) which represents a unique parameter for the level (integer and > 0, e.g. level ID).
Step 5: Overlay
- The intersection of all data layers creates small areas (specific layers can be disregarded by deselecting them). Those areas are not suitable as HRUs and should therefore be eliminated.
- For this purpose a threshold value is defined (Size of smallest area to remove) which determines the minimum size of an HRU (in cells).
- Example: A value of 8 (and an assumed solution of 25m) results in a designation of HRUs which is bigger than (8*25*25) = 5000m² =0.5ha
Step 6: Topology
- For the determination of the topological connection of HRUs (and water segments) no specific parameter input is necessary.
- The module calculates
- the N:1 topology (HRUs can drain in only one neighboring HRU/river section)
- the N:M topology (HRUs can drain in several neighboring HRUs/river sections)
- water topology (topological combination of all river sections)
- The option Enable discrete reaches is an extension of the topological derivation and its development has not yet been finished.
Step 7: Statistics
- The existing HRU map in grid format (Geo Tiff) is now converted into a shapefile. In doing so, additional features of a single HRU can be selected which are taken to the attribute chart or are supposed to be calculated.